
I did in fact set the MTU to 1400 – I like nice, round numbers – and sure enough both access points resumed proper communication with the controller. I should be able to set the MTU size on the controller to 1412 and the access points should resume functioning normally.
This leaves 88 bytes as the IPSEC header. At 1385 the packets were again rejected as being too large. The MTU size does not account for the IPSEC overhead.Īfter some testing with different packet sizes I hit on the magic number: 1384 bytes.
Packet needs to be fragmented but DF set.Įxcellent! So now to test across our IPSEC tunnel:Ĭ:\Users\netcanuck>ping 172.16.68.1 -f -l 1472 So, assuming a standard ethernet MTU of 1500, and accounting for an 8-byte ICMP header, and 20-byte IP header, I should be able to send an ICMP packet sized to 1472 bytes, but 1473 should be too large:Ĭ:\Users\netcanuck>ping 172.16.32.1 -f -l 1472 This, combined with the -l flag allows you to set the size of the ICMP packet being sent.
MTU FOR VPN MAC WINDOWS
The -f flag from a Windows command prompt prevents an ICMP packet from being fragmented. So how do I find out exactly how much our particular IPSEC configuration is adding? ping -f I needed to lower the MTU size on the controller, but to what value? IPSEC doesn’t seem to have a ‘fixed’ header size due to the different encryption options that can be used. With these sites connected via IPSEC, that was going to cause some fragmentation due to the overhead that IPSEC was going to add onto the traffic going between sites. The MTU for CAPWAP traffic between the access points and the controller is hard set by the controller to 1500*.
I opened a ticket with the wireless vendor and (very quickly) received an answer. I set up a packet debug on both sites’ firewalls and saw traffic going back and forth between the access points and the controller, and both access points appeared on the controller status window, alternating between “Provisioning” and “Disconnected”. Both access points were reachable via ping and ssh. Both AP’s repeatedly disconnected due to a “heartbeats lost” error.Ĭonnectivity between the main office and the remote sites appeared fine.
MTU FOR VPN MAC UPDATE
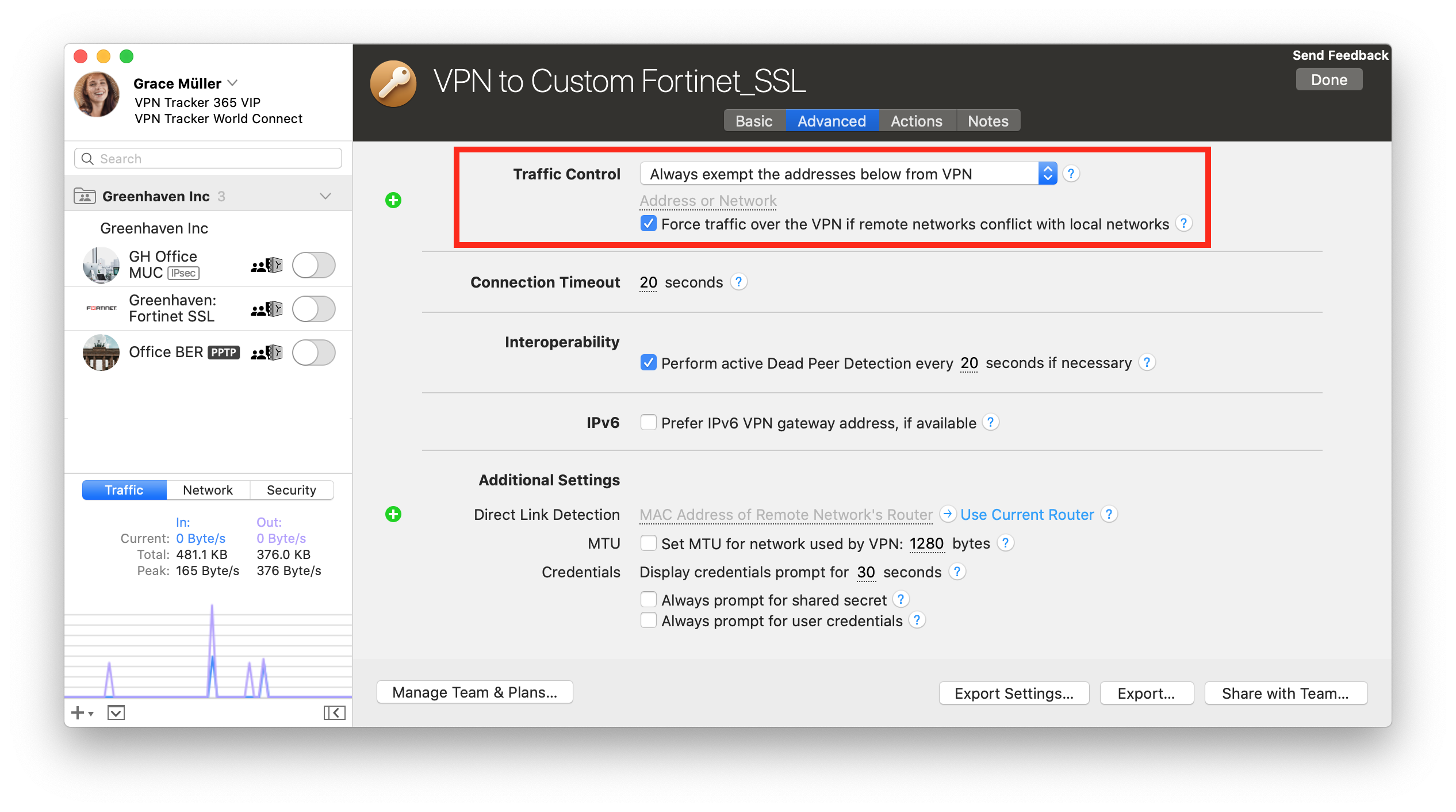
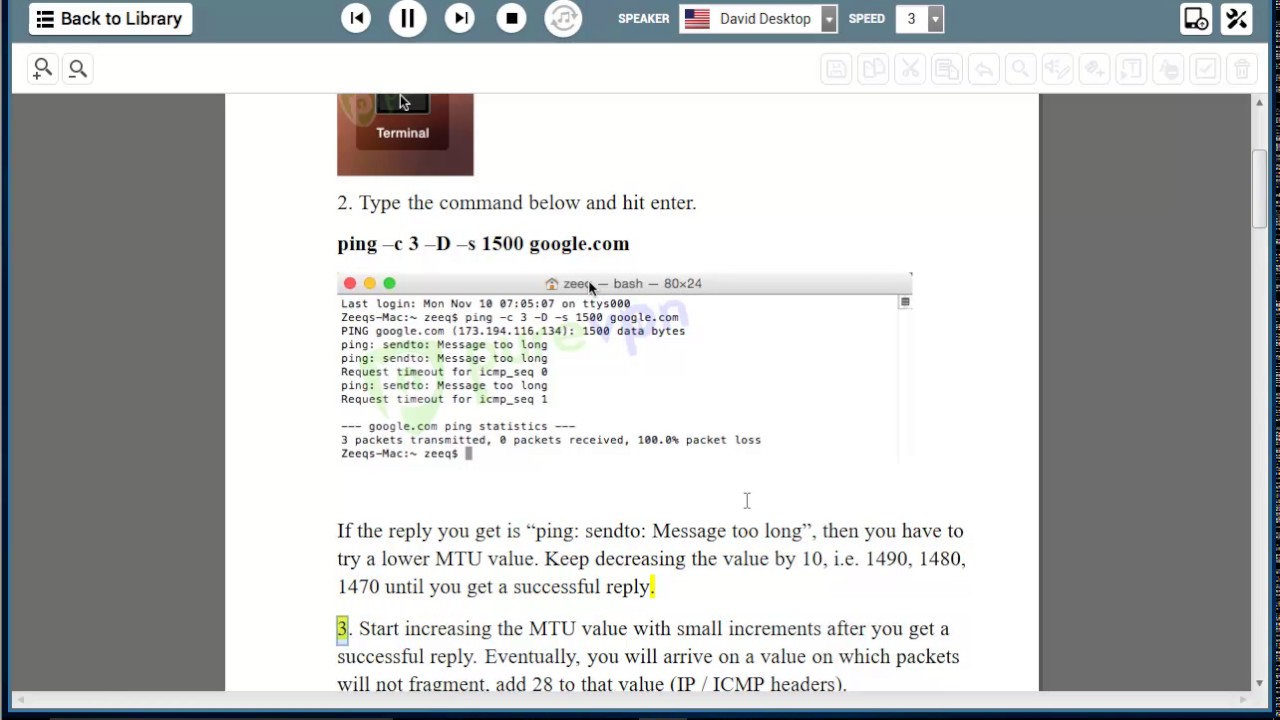
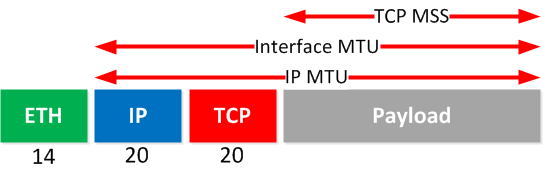
After a recent firmware update to the wireless controller both access points got stuck in a provisioning loop and appeared to have difficulty communicating with the controller. Looking for a VPN router setup? click here.I recently deployed a couple of wireless access points to two sites that connect to our main office over IPSEC VPN. 1460 + 28 = 1488 is the optimum MTU Setting.1460 Max packet size from the Ping Test.Therefore, you must add 28 to your results from the ping test. Please note that 20 bytes are added for the IP header and 8 bytes are allocated for the ICMP Echo Request Header. Now that you have the biggest packet size from the ping test, you will need to add 28 bytes. Once you’ve reached the packet size which does not fragment, increase the packet size in small increments and test again until you reach the biggest packet size possible that doesn’t fragment. If you’re getting the same results, drop the packet size down more and do the further test until you reach a packet size that does not fragment. Drop the packet size down by 10 to 20 bytes and test again.Īs you can see from the test above, our packets still need to be fragmented. You will now see your packets needs to be fragmented. Type cmd into the box and then press Ctrl+Shift+Enter on your keyboard to run the command as an administrator.Īt the Command Prompt window, type in the command below followed by the Enter key on your keyboard. Press and hold the WinKey and R button to launch the Run window. To do this, please follow the steps below: You can get the correct MTU values for your connection by simply sending out ping request and progressively lower down your packet size until it no longer needs to be fragmented. When you’re having network performance issues such as the VPN connection is being timed out. Generally, if your MTU value is too big for the connection, your computer/device will experience packet loss or drop of Internet connection. The maximum transmission unit (MTU) feature on your router allows you to determine the biggest data size permitted on your connection.
MTU FOR VPN MAC HOW TO
How To Find Correct MTU Values on Windows?


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
